Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 )
) (SrAl
(SrAl Ta
Ta O
O )
) with
with 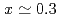
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Koda, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.25_1 - 25_7, 2024/12
Sun, Haomin; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Yokomine, Takehiko*; Shen, X.*; Hibiki, Takashi*
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 154, p.111171_1 - 111171_24, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q. H.*; Fang, X.*; Wang, Q. M.*; Ma, Y.*; Tachi, Yukio
Sedimentary Geology, 465, p.106633_1 - 106633_14, 2024/05
 Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillation
Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillationOuchi, Kazuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Hirose, Kazuki*; Kurosawa, Yuika*; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shibukawa, Masami*; Saito, Shingo*
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1298, p.342399_1 - 342399_7, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0Given that conventional methods of high-dose sample analysis pose substantial exposure risks and generate large amounts of secondary radioactive waste, faster procedures allowing for decreased radiation emission are highly desirable. To address this need, we developed a  Sr
Sr quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed
quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed  Sr
Sr in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify
in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify  Sr
Sr in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
Irisawa, Eriko; Kato, Chiaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 591, p.154914_1 - 154914_10, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The amount of corrosion of austenitic stainless-steel R-SUS304ULC was evaluated considering the changes in solution composition and boiling during actual concentration operations. Austenitic stainless-steel R-SUS304ULC is the structural material of the highly radioactive liquid waste concentrator in Japanese spent fuel reprocessing plant, which treats highly corrosive nitric acid solutions during enrichment operations. The study results show that it is necessary to focus on nitric acid concentrations, oxidizing metal ion concentrations, and decompression boiling as factors that accelerate the corrosion rate of stainless steel because of cathodic reaction activation.
Group for Fukushima Mapping Project
JAEA-Technology 2023-024, 176 Pages, 2024/03
This report presents results of the investigations on the distribution-mapping project of radioactive substances owing to TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) conducted in FY2022. Car-borne surveys, a measurement using survey meters, a walk survey and an unmanned helicopter survey were carried out to obtain air dose rate data to create their distribution maps, and temporal changes of the air dose rates were analyzed. Surveys on depth profile of radiocesium and in-situ measurements as for radiocesium deposition were performed. Based on these measurement results, effective half-lives of the temporal changes in the air dose rates and the deposition were evaluated. Score maps to classify the importance of the measurement points were created, and the factors causing changes in the score when monitoring data from multiple years were used were discussed. The range of fluctuation of past tritium concentration data in seawater was determined, and the causes of the fluctuation were discussed. Monitoring data in coastal area performed in 2022 owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan was summarized, and temporal changes in cesium-137 were analyzed. Using the Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach, we obtained maps that integrated air dose rate distribution data acquired through surveys such as car-borne and walk surveys with respect to the region within 80 km from the FDNPS and Fukushima Prefecture. The measurement results for FY2022 were published on the "Database for Radioactive Substance Monitoring Data", and measurement data were stored as CSV format. Radiation monitoring and analysis of environmental samples owing to the comprehensive radiation monitoring plan were carried out.
Yamashita, Kiyoto; Maki, Shota; Yokosuka, Kazuhiro; Fukui, Masahiro; Iemura, Keisuke
JAEA-Technology 2023-023, 97 Pages, 2024/03
The incinerator adopted to incineration room, Plutonium Waste Treatment Facility had been demonstrated since 2002 for developing technologies to reduce the volume of fire-resistant wastes such as vinyl chloride (represented by Polyvinyl chloride bags) and rubber gloves for Radio Isotope among radioactive solid wastes generated by the production of mixed oxide fuels. The incinerator, cooling tower, and processing pipes were replaced with a suspension period from 2018 to 2022, which fireproof materials on the inner wall of the incinerator was cracked and grown caused by hydrogen chloride generated when disposing of fire-resistant wastes. This facility consists of the waste feed process, the incineration process, the waste gas treatment process, and the ash removal process. We replaced the cooling tower in the waste gas treatment process from March 2020 to March 2021, and the incinerator in the incineration process from January 2021 to February 2022. In addition, samples were collected from the incinerator and the cooling tower during the removing and dismantling of the replaced devices, observed by Scanning Electron Microscope and X-ray microanalyzer, and analyzed by X-ray diffraction to investigate the corrosion and deterioration of them. This report describes the method of setting up the green house, the procedure for replacing them, and the results from analysis in corrosion and deterioration of the cooling tower and incinerator.
Togawa, Orihiko; Okuno, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2023-043, 94 Pages, 2024/03
In order to translate nuclear disaster prevention documents written in Japanese into English, the Basic Act on Disaster Management, the Act on Special Measures Concerning Nuclear Emergency Preparedness, and the Convention on Nuclear Safety were surveyed for corresponding terms in Japanese and English. The survey results were integrated and unified English translations were selected. As a result, a Japanese-English correspondence table of technical terms in the field of nuclear disaster prevention was prepared and proposed.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2023-030, 80 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a cooperative operation robot system for radiation source exploration" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to develop a Cooperative Operation Robot system for RAdiation Source Exploration (CORRASE). The multiple robot system provides radiation source exploration with wide field of view, rapidity, and low cost. The radiation source exploration is realized with multiple robots carrying directional gamma-ray detectors determining the incident direction of the incoming gamma-rays. We will develop the system by the final year of this proposal aiming for application in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Kyoto University*
JAEA-Review 2023-028, 54 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2022, this report summarizes the research results of the "Establishment of 3-D dose dispersion forecasting method and development of in-structure survey using the transparency difference of each line gamma-ray" conducted in FY2022. We realized an electron track detecting Compton camera (ETCC) that can measure  -ray images (linear images) with the bijective projection. In the "Quantitative analysis of radioactivity distribution by imaging of high radiation field environment using gamma-ray imaging spectroscopy" (hereinafter referred to as the previous project) adopted in FY2018, the 1 km square area including the reactor buildings was imaged at once.
-ray images (linear images) with the bijective projection. In the "Quantitative analysis of radioactivity distribution by imaging of high radiation field environment using gamma-ray imaging spectroscopy" (hereinafter referred to as the previous project) adopted in FY2018, the 1 km square area including the reactor buildings was imaged at once.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Hokkaido University*
JAEA-Review 2023-027, 126 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study on rational treatment/disposal of contaminated concrete waste considering leaching alteration" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to understand migration behaviors of radionuclides in relation to the properties of concrete altered by leaching, to develop migration model of radionuclides, and to evaluate waste management scenarios, focusing on underground concrete structures in contact with contaminated water.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2023-023, 99 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human Resource Development Related to Remote Control Technology for Monitoring Inside RPV Pedestal during Retrieval of Fuel Debris" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to construct a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2022, each system was improved and expanded toward the final year, and verification experiments were conducted in simulated environments.
Togawa, Orihiko; Hokama, Tomonori; Hiraoka, Hirokazu; Saito, Shota
JAEA-Research 2023-011, 78 Pages, 2024/03
When radionuclides are released into the atmospheric environment at a nuclear emergency, protective measures such as evacuation and temporal relocation are carried out using motor vehicles such as private cars and buses to reduce radiation exposure to residents. To confirm conditions of contamination for the evacuated/relocated residents and the used motor vehicles, contamination inspection is conducted in the middle of the route from border areas of Nuclear Emergency Planning Zone to evacuation shelters. In the present inspection in Japan, a value of OIL4 = 40,000 cpm is used as decontamination criteria. For the details and derivation methods of the value, however, no official documents are found which give systematically detailed descriptions and explanation. It is also recognized that even few experts on nuclear emergencies can explain these subjects in detail as a whole. In order to explain scientifically and technically the OIL4 value of decontamination criteria used in contamination inspection in Japan, this report aims at investigating and estimating the deviation methods of OIL4, and examining and considering these results. To achieve the objectives, we show the bases for decontamination criteria, and investigate and estimate the derivation methods for limits of a surface contamination density corresponding to the generic criteria for each exposure pathway. Moreover, we give the OIL4 value some consideration and suggestions from a viewpoint of positioning and feature of OIL4 in Japan, and cautionary points at revising the value.
 -Ga
-Ga O
O (001)
(001)Tsai, Y. H.*; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tanida, Hajime; Kobayashi, Toru; Yamashita, Yoshiyuki*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(11), p.112105_1 - 112105_5, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0Murakami, Kenta*; Arai, Taku*; Yamada, Koji*; Momma, Kensuke*; Tsuji, Takashi*; Nakagawa, Nobuyuki*; Onizawa, Kunio
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2024/03
This paper studied the future vision of codes and standards in Japan by systematically comparing Japanese regulatory rules, standards, and industry guides related to long term operation with international safety standards, and confirmed that the Japanese standard system generally meets their recommendations. The recommendation for the future improvements of Japanese codes and standards were summarized into five items.
Project Promotion Department; Radioactive Wastes Disposal Center
JAEA-Review 2023-037, 162 Pages, 2024/02
For near surface disposal of radioactive wastes generated from research, industrial and medical facilities, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has discussed methods for corresponding to the technical standards on confirmation related to waste disposal, etc. From FY2022, we have established Waste Standards Committee and interim Waste Acceptance Criteria, Waste Package Confirmation Procedure, etc. have been considered. In FY2022, Waste Package Confirmation Procedures of solidified liquid waste and cement filled waste and related standards were discussed. In addition, issues of preparation of Waste Package Confirmation Procedure and rational treatment method for decommissioning wastes were considered. This annual report summarizes the results of discussion in FY2022.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Ibaraki University*
JAEA-Review 2023-021, 112 Pages, 2024/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Contribution to Risk Reduction in Decommissioning Works by the Elucidation of Basic Property of Radioactive Microparticles" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). The present study aims to understand the basic properties (size, chemical composition, isotopic composition - including concentration of  -emitters, electrostatic properties, and optical properties, etc.) of fine particles composed of silicate with insoluble properties which contain regions of highly concentrated radioactive cesium (Cs) released to the environment by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of TEPCO in 2011 March.
-emitters, electrostatic properties, and optical properties, etc.) of fine particles composed of silicate with insoluble properties which contain regions of highly concentrated radioactive cesium (Cs) released to the environment by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of TEPCO in 2011 March.
Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ono, Takahiro; Kakutani, Satomi; Yoshida, Moeka; Suzuki, Soichiro
Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, 36(1), p.125 - 133, 2024/02
The Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development was established for the purpose of developing and verifying remote control equipment for promoting the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and the external use of this center was started in 2016. The mission of this center is to contribute to the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and for the reconstruction of Fukushima Prefecture. In this review, we describe the equipment related to the full-scale mock-up test, the component test for a remote-control device and the virtual reality system in this center. In addition, the case examples for usage of these equipment are introduced.
Nakamura, Keita; Hanari, Toshihide; Matsumoto, Taku; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Yashiro, Hiroshi*
Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, 36(1), p.115 - 124, 2024/02
Hata, Koji*; Niunoya, Sumio*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Miyara, Nobukatsu*
Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 16(2), p.365 - 378, 2024/02
Excavation of underground caverns, such as mountain tunnels and energy-storage caverns, may cause the damages to the surrounding rock as a result of the stress redistribution. In this influenced zone, new cracks and discontinuities are created or propagate in the rock mass. Therefore, it is effective to measure and evaluate the acoustic emission (AE) events generated by the rocks, which is a small elastic vibration, and permeability change. The authors have developed a long-term measurement device that incorporates an optical AE (O-AE) sensor, an optical pore pressure sensor, and an optical temperature sensor in a single multi-optical measurement probe (MOP). Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting R&D activities to enhance the reliability of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) deep geological disposal technology. In a high-level radioactive disposal project, one of the challenges is the development of methods for long-term monitoring of rock mass behavior. Therefore, in January 2014, the long-term measurements of the hydro-mechanical behavior of the rock mass were launched using the developed MOP in the vicinity of 350 m below the surface at the Horonobe Underground Research Center. The measurement results show that AEs occur frequently up to 1.5 m from the wall during excavation. In addition, hydraulic conductivity increased by 2 to 4 orders of magnitude. Elastoplastic analysis revealed that the hydraulic behavior of the rock mass affected the pore pressure fluctuations and caused micro-fractures. Based on this, a conceptual model is developed to represent the excavation damaged zone (EDZ), which contributes to the safe geological disposal of radioactive waste.